Education System of AMERICA

@Tragicfonts, @Infodeaofficial
Schooling is compulsory for all children in the America. But the age range for which school attendance is required varies from state to state. Some states allow students to leave school between 14 and 17 with parental permission, before finishing high school; other states require students to stay in school until age 18. Free education basically starts from kindergarten to grade 12 (frequently abbreviated K-12). Children who do not comply with compulsory attendance laws without good cause are deemed to be truants, and they and their parents may be subject to various penalties under state law.

Most parents send their children to either a public or private institution. According to government data, one-tenth of students are enrolled in private schools. Approximately 85% of students enter the public schools, largely because they are tax-subsidized (tax burdens by school districts vary from area to area). School districts are usually separate from other local jurisdictions, with independent officials and budgets.
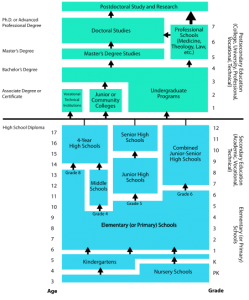
Most children begin elementary education with kindergarten (usually five to six years old) and finish secondary education with twelfth grade (usually 17–18 years old). In some cases, pupils may be promoted beyond the next regular grade. Parents may also choose to educate their own children at home; 1.7% of children are educated in this manner.
The country has been outrun, the study says, by other nations because the US has not done enough to encourage the highest achievers.
About half of the states encourage schools to make their students recite the Pledge of Allegiance to the flag daily.
Teacher works about 35 to 46 hours a week, according a survey taken in 1993. In 2011, American teachers worked 1,097 hours in the classroom, the most for any industrialized country measured by its Organisation in Economic Co-operation and Development. They spend 1,913 hours a year on their work, just below the national average of 1,932 hours for all workers. In 2011, the average annual salary of a pre-K–12 teacher was $55,040.
Grade placement
Schools use several methods to determine grade placement. Some methods are placing students in a grade based on a child’s birthday. Cut off dates based on the child’s birthday determine placement in either a higher or lower grade level. For example, if the school’s cut-off date is September 1, and an incoming student’s birthday is August 2, then this student would be placed in a higher grade level. If the student is in high school, this can lead to the student gets placed in 11th grade instead of a 10th because of their birthday. Content each grade aligns with age and academic goals for the expected age of the students. Generally, a student is expected to advance a grade each year K-12; however, if a student under-performs, he or she may retake that grade.
Secondary Education
Secondary education is often divided into two phases, middle/junior high school and high school. Students are usually given more independence, moving to different classrooms for different subjects, and being allowed to choose some of their class subjects (electives).
“Middle school” (or “junior high school”) has a variable range between districts. It usually includes seventh and eighth grades and occasionally also includes one or more of the sixth, ninth, and very occasionally fifth grades as well. High school includes grades 9 through 12. Students in these grades are commonly referred to as freshmen (grade 9), sophomores (grade 10), juniors (grade 11) and seniors (grade 12). At the high school level, students generally take a broad variety of classes without specializing in any particular subject, with the exception of vocational schools. Students are generally required to take a broad range of mandatory subjects, but may choose additional subjects (“electives”) to fill out their required hours of learning. High school grades are also be mention in a student’s official transcript, e.g. For college admission. Official transcripts usually include the ninth grade, whether it is taught in a middle school or a high school.
Governance
Currently, the state and national governments share power over public education, with the states exercising most of the control. Except for Hawaii, the state delegate power to county, city or township-level school boards that exercise control over a school district. Some school districts may further delegate significant authority to principals, such as those who have adopted the Portfolio strategy.
The U.S. federal government exercises its control through the U.S. Department of Education. Education is not mentioned in the constitution of the United States, but the federal government uses the threat of decreased funding to enforce laws pertaining to education. Under recent administrations, initiatives such as the No Child Left Behind Act and Race to the Top have attempted to assert more central control in a heavily decentralized system.
Non-profit private schools are widespread, are largely independent of the government, and include secular as well as parochial schools. Educational accreditation decisions for private schools are made by voluntary regional associations.
As compared to many other countries the education system of U.S is far more better, and other countries should take inspiration and develop their education ministry.




